Did you know nearly half of all pregnancies in the U.S. are considered unplanned pregnancies? According to National Health Statistics Reports, this is one reason why more people are looking for safe and reliable non-hormonal birth control options non-hormonal. For many, avoiding hormones is about reducing side effects like mood swings, weight gain, or the small but serious risk of blood clots. For others, it’s about finding a method that works better with their health, lifestyle, or fertility goals.
This guide will walk you through the most common non-hormonal contraception choices available today. From the copper IUD and barrier methods to fertility awareness-based methods and permanent procedures like tubal ligation, you’ll see how each option works, its effectiveness, pros and cons, and who it may be best for.
What Is Non-Hormonal Birth Control?
Non-hormonal birth control includes any contraceptive methods women and men can use that don’t rely on hormones to prevent pregnancy. Instead of preventing ovulation like hormonal birth control options such as the birth control pill or other forms of hormonal contraception, these methods work in different ways. They may block sperm from reaching the egg through barrier contraceptives like male condoms, female condoms, cervical caps, or the contraceptive sponge. Others, such as the copper intrauterine device (IUD), make the uterus unfriendly for sperm or eggs, reducing the chance of fertilization.
In addition, some people choose fertility awareness methods, also known as natural family planning, which involve tracking the menstrual cycle, vaginal discharge, cervical mucus, and basal body temperature to predict ovulation. For those seeking a more permanent solution, procedures like female sterilization or vasectomy block the fallopian tubes or vas deferens to provide lifelong protection. Because these non-hormonal methods don’t alter your hormone levels or disrupt your menstrual period, they are often appealing to individuals who prefer natural choices, are breastfeeding, or cannot safely use hormones due to medical history, such as a risk of blood clots or certain cancers.
Why Choose Non-Hormonal Birth Control?
People consider non-hormonal methods for many reasons:
- Avoiding side effects from hormones: mood changes, headaches, or menstrual bleeding changes.
- Breastfeeding safety: Non-hormonal choices won’t affect milk supply.
- Medical conditions: safer for those at risk of blood clots, heart disease, or certain cancers.
- Lifestyle fit: Some people prefer hormone-free contraceptive methods that women can control directly.
- Permanent solutions: Sterilization offers lifelong protection.
Types of Non-Hormonal Birth Control
Several types of non-hormonal birth control offer safe and effective ways to prevent pregnancy without affecting your natural hormones. These methods range from short-term options like barrier contraceptives to long-lasting solutions such as the copper IUD or even permanent procedures.
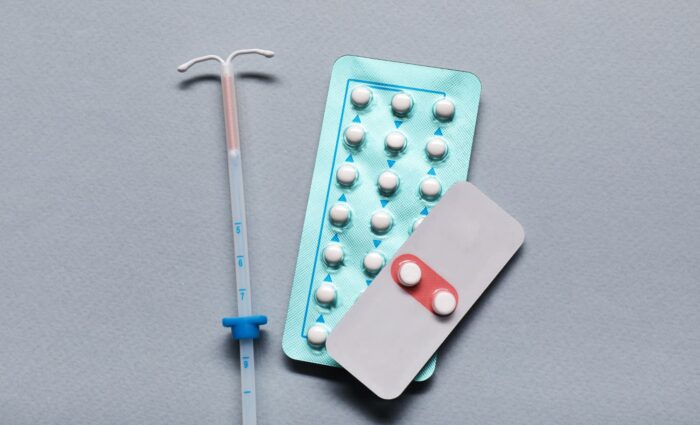
Copper IUD (Copper Intrauterine Device)
The copper IUD is a small, T-shaped device placed inside the uterus by a healthcare provider. It works by releasing copper ions that prevent sperm from fertilizing the egg. This makes it one of the most effective forms of non-hormonal birth control, with an effectiveness rate of over 99%. This intrauterine device can last up to 10 years, offering a long-term and reversible option. It may also serve as emergency contraception if inserted within 5 days of unprotected sex. However, it may cause heavier menstrual periods, cramps, or spotting, and in rare cases can lead to ectopic pregnancy or uterine perforation.
Barrier Methods
Barrier contraceptives work by physically blocking sperm from entering the uterus and include several widely used options. Male condoms (external condoms) are about 87–98% effective and remain the only method that also helps prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). On the other hand, female condoms (internal condoms) are 79–95% effective and also reduce the risk of STIs. Other methods include the cervical cap, which fits over the cervix and is used with spermicide, with an effectiveness rate of 78–85%. The diaphragm, a silicone dome also paired with spermicide, has an effectiveness rate of 86–94%. The contraceptive sponge, which contains spermicide and is inserted before sex, is 76–91% effective. These barrier methods are easy to access, non-invasive, and many protect against STIs, though they must be used correctly every time and may cause allergic reactions or increase the risk of urinary tract infections.
Spermicides and Vaginal Gels
Spermicides are chemicals that kill or disable sperm and come in forms such as gels, foams, creams, or suppositories, while the vaginal gel (Phexxi) works by lowering vaginal pH to make it harder for sperm to survive. On their own, spermicides are about 70% effective, but when combined with barrier methods, their effectiveness increases to 93–94%. These non-hormonal birth control options are available over the counter and can be used on demand, making them convenient and accessible. However, they do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and may cause irritation. Frequent use can also raise the risk of urinary tract infections, which is why many people consult an OB-GYN or family medicine provider before relying on spermicides alone.
Fertility Awareness-Based Methods & Natural Family Planning
Also called fertility awareness-based methods or natural family planning, these approaches involve tracking the menstrual cycle and fertility signs. These signs include basal body temperature, vaginal discharge, and cervical mucus. Techniques include the calendar or rhythm method and apps or devices that help predict ovulation. With an effectiveness of 75–88% in regular cycles, these methods are natural, hormone-free, and low-cost, but they require daily attention, are less reliable with irregular cycles, and do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Because accuracy is key, many people review their plan with an OB-GYN to ensure correct use.
Behavioral Methods
Behavioral methods of non-hormonal birth control include the withdrawal method (pull-out method), where the penis is withdrawn before ejaculation. This method has an effectiveness rate of about 78%. Another option is outercourse (non-penetrative sex), which can be 100% effective at avoiding pregnancy if penetration is completely avoided. These methods are free and accessible anytime, but they carry a high failure rate in practice and offer no protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Permanent Non-Hormonal Methods (Sterilization)
For those seeking a permanent procedure, female sterilization through tubal ligation or salpingectomy blocks or removes the fallopian tubes, preventing sperm and egg from meeting. A vasectomy (male sterilization) seals the vas deferens to prevent sperm release. Both methods are nearly 100% effective at preventing pregnancy, making them among the most reliable non-hormonal birth control options. The advantages include permanence and no ongoing costs, but they are considered irreversible, require a surgical procedure, and do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Emergency Contraception Without Hormones
The copper IUD is the most effective form of non-hormonal emergency contraception, working if inserted by a healthcare provider within 5 days after unprotected sex. It is far more effective at preventing an unintended pregnancy than hormonal methods such as emergency pills like Plan B, making it the best choice for those seeking reliable, hormone-free protection after unprotected intercourse.
Comparison Table – Non-Hormonal Birth Control
| Method | Effectiveness | Protects Against STIs | Duration | Notes |
| Copper IUD | >99% | No | 5–10 years | Can be used as emergency contraception |
| Male condoms | 87–98% | Yes | Single use | Accessible, over-the-counter |
| Female condoms | 79–95% | Yes | Single use | May feel less natural |
| Cervical cap | 78–85% | No | Up to 2 years | Use with spermicide |
| Diaphragm | 86–94% | No | 1 year reusable | Must remain for 6 hrs post-sex |
| Sponge | 76–91% | No | 24 hours | Higher risk of infection |
| Spermicide / Vaginal gel | 70–93% | No | Single use | Best with barrier methods |
| Natural family planning | 75–88% | No | Daily monitoring | Requires discipline |
| Withdrawal method | ~78% | No | Per act | High risk of failure |
| Sterilization | ~100% | No | Permanent | Surgical procedure |
Conclusion
There are many safe and effective non-hormonal contraception choices to consider, from short-term barrier methods to long-lasting protection with the copper IUD, and even permanent procedures like female sterilization. The best method ultimately depends on your health, lifestyle, and family planning goals, so it’s important to choose an option that fits your needs and provides peace of mind.
At Rego Park Diagnostic & Treatment Center, we provide expert women’s health and family planning services to help you find the right birth control method. Whether you’re exploring non-hormonal options or comparing them with other methods, our team is here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the next step toward safe, reliable contraception.
FAQs
What is the best non-hormonal birth control method?
The best non-hormonal birth control method is the copper IUD, which is over 99% effective, long-lasting, and completely hormone-free.
What’s the healthiest form of birth control?
What’s the healthiest form of birth control depends on your health and lifestyle, but many consider the copper IUD or barrier methods like condoms healthy options since they avoid hormones.
What birth control pill does not have hormones?
There is no traditional birth control pill that does not have hormones, but non-hormonal methods such as the copper IUD, condoms, or natural family planning are alternatives.
How painful is an IUD?
How painful an IUD is depends on the individual, but most people experience cramping during insertion; discomfort usually improves within a few days.